11 Key Differences Between WiFi and LiFi You Need to Know
Published: 4 Sep 2025
Did you know that WiFi and LiFi are two of the most widely discussed wireless communication technologies in the world today? Millions of people use them every day to stay connected to the internet, yet many people don’t completely comprehend the differences.
In this blog post, we will explore the differences between LiFi (Light Fidelity) and WiFi Wireless Fidelity) in simple words to help you understand how these technologies work and how they play special roles in our connected world.
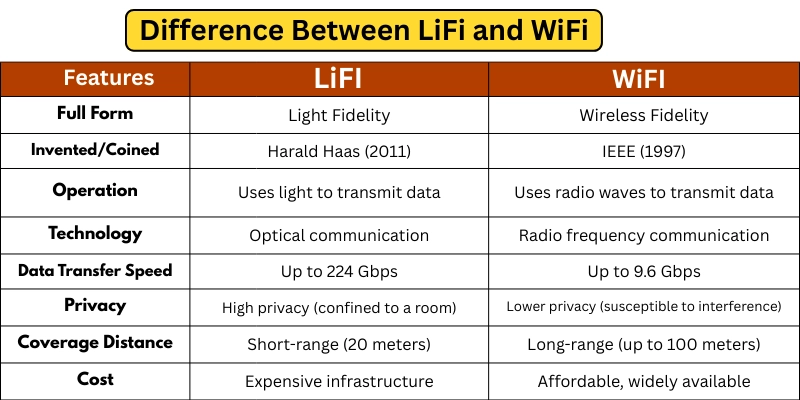
11 Differences between LiFi and WiF
The difference between LiFi and WiFi is important to understand since they are both wireless communication technologies that work in quite different ways. The following is a list of the essential dissimilarities between these two technologies.
- Full Form
- Invented/Coined
- Operation
- Technology
- Data Transfer Speed
- Privacy
- Coverage Distance
- Cost
- Merits
- Demerits
- Applications
Full Form
Wifi and Lifi have different full forms. Let’s find out what each one stands for and what it means.
WiFi
It stands for Wireless Fidelity, which allows devices to connect to the internet wirelessly using radio waves.
LiFi
It stands for Light Fidelity, which uses light waves instead of radio waves to transmit data.
Invented/Coined
WiFi
Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) was invented by the NCR Corporation in 1991. It quickly became the preferred technology for wireless internet connections worldwide.
LiFi
Light Fidelity (LiFi) was developed by Professor Harald Haas in 2011. Haas introduced LiFi as a way to provide high-speed internet using light instead of radio waves.
Operation
WiFi
The WiFi device sends data through radio waves to a WiFi router. These radio waves travel across the air and reach a variety of devices, including cellphones, computers, and tablets.
LiFi
The LiFi operates through LED lights. It modulates light emitted by LEDs at high speeds to carry data. The device receiving the data must be within line-of-sight of the light source.
Technology
WiFi
The technology of WiFi is based on WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) technology using 802.11 standards (like 802.11b/g/n/ac).
LiFi
Visible Light Communication (VLC) technology is used in Lifi with standards such as IEEE 802.15.7, enabling devices to transmit data through light signals.
Data Transfer Speed
WiFi
WiFi devices normally provides data speeds up to 1 Gbps. However, this may change based on the router type, network situations, and interference.
LiFi
LiFi has the potential to provide significantly faster speeds up to 100 Gbps or more, making it ideal for transferring big files or watching high-resolution entertainment.
Privacy
WiFi
WiFi signals can pass through barriers, making it easier for hackers or unauthorized users to capture data. Safety precautions, such as WPA3 encryption, are required to ensure safe data transport.
LiFi
LiFi communicates via visible light, which cannot break through barriers. This increases security by limiting access to anybody within the line of sight of the light source.
Coverage Distance
WiFi
WiFi has a larger coverage range, often 30-50 meters in open settings, depending on the router and the outside environment. It can also travel through barriers, allowing it to reach greater distances.
LiFi
LiFi has a very limited range, often 10 meters or less, and needs direct view. This detail suggests that it works best in a room or a small, contained location.
Cost
WiFi
WiFi is more readily accessible and reasonably priced. Wi-Fi infrastructure, such as routers as well as connection points is affordable and widely available in homes, workplaces, and public locations.
LiFi
LiFi is now more costly to set up. It demands specialized equipment, such as LED lights with embedded transmitters and photodetectors. However, with the progress in technology the costs of LiFi are expected to fall.
Merits
Here are some advantages of WiFi vs LiFi.
WiFi
- Covers large areas, making it suitable for homes, offices, and public places.
- Easy to set up since many devices already support WiFi.
- Allows you to stay connected anywhere within a range of devices.
LiFi
- Offers very fast data transfer speeds, potentially reaching up to 100 Gbps.
- Provides higher security since light doesn’t go through walls.
- Consumes less power, especially in spaces with LED lighting.
- Faces less interference from other electronic devices because it uses light waves instead of radio waves.
Demerits
Here are some disadvantages of WiFi and LiFi.
WiFi
- It faces interference from other devices (like microwaves and Bluetooth) and physical barriers (such as walls).
- It can be insecure because signals may be blocked over long distances.
- It is less reliable in crowded environments where many devices connect.
LiFi
- It has a limited range because it needs a direct line of sight for communication.
- It doesn’t work well in outdoor settings or places with bright ambient lighting.
- It is still developing, so infrastructure use is not yet available, making it less practical in many situations.
Applications
Here are some common applications of WiFi and Li-Fi.
WiFi
- Home Networking: Connects phones, laptops, and other smart devices.
- Public WiFi hotspots: Available in cafes, airports, and hotels for internet access.
- Office and business use: Helps with team collaboration, meetings, and customer service.
LiFi
- Specialized Environments: LiFi works well in hospitals, offices, and airports where fast and secure communication is needed.
- Smart Cities: LiFi can provide internet connectivity in busy urban areas with many people.
- Underwater Communication: LiFi can transmit data underwater without being affected by saltwater interference.
Conclusion
So technology lovers, it’s time to finish up! In this article, we’ve covered the 11 key differences between LiFi and WiFi in detail. Understanding these differences will help you appreciate how each technology plays a unique role in our connected world.
Knowing when to use LiFi or WiFi will make a big difference, whether you want faster speeds, better security, or broader service. Want to learn more about the latest technologies? Please take a look at our other articles!
Questions about the difference Between LiFi and WiFi
Here are common queries people also ask about LiFi vs WiFi:
No, LiFi is not necessarily better than WiFi. LiFi has more protection and faster speeds, but it has a short range and needs a clear line of sight to communicate. WiFi is more adaptable for long-range use and works through walls.
No, LiFi cannot travel through walls. Walls and other physical barriers can block its signals because it sends data through light waves.
LiFi hasn’t gained widespread adoption due to its limited range and the need for face-to-face communication. Furthermore, creating the required infrastructure is more expensive than WiFi.
Currently, most phones don’t support LiFi. However, future phones could potentially be provided with LiFi capabilities with the necessary hardware.
No, LiFi will not completely replace WiFi. It is more likely to go along with WiFi to be utilized for high-speed, secure connectivity in specific settings. At the same time, WiFi continues to be used for general-purpose internet access.
LiFi can be affected by sunlight. The bright light from the sun can interfere with the light signals used by LiFi, reducing its effectiveness for outdoor environments.
LiFi was invented in the UK by Professor Harald Haas in 2011. He revealed the potential of using light to transmit data at high speeds.
WiFi uses radio waves to transmit data and works over longer distances, including through walls.
LiFi uses light to send data and requires face-to-face conversation but can provide much faster speeds and higher security.
LiFi is faster than WiFi because light waves can carry far more data than radio waves. Light has a much higher frequency, allowing for greater data transfer speeds, making LiFi potentially 100 times faster than WiFi.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks